excise tax
ad valorem property tax
sales tax
value added tax
user fees
withholdings; social insuarance payments; parafiscal charges
gross income
adjusted gross income
deductions
tax credits
depreciation
tax base
tax basis
tax incidence
tax rate
fiscal
budgetary
monetary
What is income?
“Any source derived”
Income taxed on personality, not source principle.
Default presumption: Unless exempted, it’s taxed.
tax transparency similar to pass through entity
-subchapter s corporation
-partnerhships
tranche bracket steuerklasse
steuerdurchgriff
Gross Income
– Deductions (exclusions)
* Tax rate
– Tax Credits
= Tax due
10,000-5,000=5000
5000*10%=500
500-250=250
Step transactions
–the law will disregard illusory transactions designed to dissimulate income
Sham transactions
Fiscal realism
Abuse of the law
Recharacterizations
examples: fictitious sale-leasebacks
“gifts” which are compensation or which do not transfer use.
How not to have it characterized as a sham?
*Transfer of equitable, not merely legal title.
*Arms length transaction – market rates.
Tax deductions
charitable donations!
*education
*health
*religion
orphans, widows, military
anything with a social justification
*stamp collecting? no.
Interest payments on loans.
weatherization/home improvements
*fringe benefits are excluded from income
-company meals
-company uniform
-company car – if used for business!
-de minimus
*ordinary and necessary business expenses are deducted from income
-uniform
– interest payments
Tax rate
Marginal tax rate
Deductions/Exclusions from Income
-ordinary and necessary business expenses
-interest payments
-depreciation
-charitable donations
-insurance payments
-capital losses up to 3000 dollars
Tax Credits
may or may not generate a refund depending on the credit.
-Solar
-Insulation
-Earned Income Tax Credit
Capital Goods
Long term capital gains
Long term capital losses
15% for stocks, 21% for real estate 28% for collectibles (gold coins, stamps)
Depreciation
Depreciation recapture is the USA Internal Revenue Service (IRS) procedure for collecting income tax on a gain realized by a taxpayer when the taxpayer disposes of an asset that had previously provided an offset to ordinary income for the taxpayer through depreciation. In other words, because the IRS allows a taxpayer to deduct the depreciation of an asset from the taxpayer’s ordinary income, the taxpayer has to report any gain from the disposal of the asset (up to the recomputed basis) as ordinary income, not as a capital gain.
year one 5 year straight line of 1000 =
y1 y2 y3 y4 y5
200 200 200 200 200 depreciation deductible from gross income.
double declining
year one 40%
1000 600 360 216 129.6
400 240 144 86.4 129.6
depreciation is a tax deduction!
we tax INCOME NOT CAPITAL.
Graphs
Flat Proportional Progressive
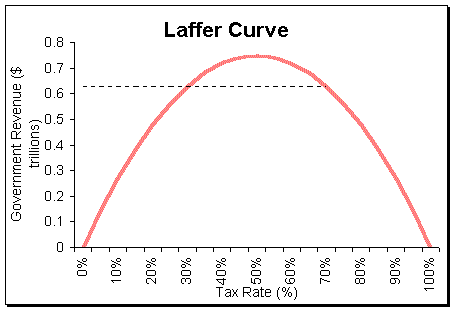
Laffer Curve
Hixson’s Helix
Realization events
Mergers
Stock-for-Stock
Cash-for-Stock — realization event
Cash-for-assets — realization event
Stock for assets
— Voting stock for assets not a realization event
Mixed: Cash and Stock for assets or stock
Up to 20% of the assets may be “boot”
Boot = non-voting stock.
With proper planning Most mergers can be structured to avoid tax liability.
-Debt
-Equity
Inflation’s effect on the economy
MACROECONOMICS
“Washington Consensus” — neoliberalism 1980-2007
*Monetary Policy
-fiat currency
-low to no inflation
–deflation is bad too obviously.
–hyperinflation is terrible because it prevents investment destroying the economy.
-monetary policy is not the best macroeconomic influence
–it’s easy to inflate a currency but difficult to deflate it.
-prime lending rate is the only effective macroeconomic influence
–tax policy is the better macroeconomic influencer
*Fiscal Policy
-Rich people reinvest surplus which grows the economy
-Poor people waste surplus on binges
–thus there is no point doing anything to alleviate poverty.
-It is easier to borrow money than to tax.
–tax (equity…)
–borrowing (debt…)
*Budgetary policy
-Balanced budgets?
*Trade policy
-trade imbalances are acceptable
-liberalisation: free movement of goods — WTO and capital
-replacing the impoverished world of autarchic warlike national economies with a world of interdependence to build peace by interdependence and prosperity.
*Supply drives demand, not the other way around.
*Economic planning is impossible and counterproductive
*Privatization is more efficient than state run industry due to competition
*Regulation generally impedes commerce
How to value a corporation
p/e – price to earnings (not to useful. division by useful. Most popular. People are dumb.)
dps – dividends per share
eps – earnings per share
debt/equity – debt to equity
Tax Vocabulary
What is adjusted gross income?
Gross income minus deductions. Section 62
What is taxable income?
Gross income minus deductions other than the standard deduction. For those who do not itemize deductions it means AGI minus standard deduction and the deduction for personal exemption.
What is a capital gain or loss?
Gain or loss from the sale or exchange of a capital asset
What is a capital asset?
Any property other than inventory
What is inventory?
Property held by the taxpayer primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of the taxpayer’s business.
What is a long-term capital gain?
Gain on property held for more than 1 year
What is short-term capital gain?
Gain on property held for one year or less
What are the netting rules?
Capital losses can offset capital gain. Up to $3K of capital losses can be used to offset ordinary income.
What is realization?
There has been some change in circumstance so that gain or loss might be taken into account for tax purposes. (i.e. sale or exchange)
What is recognition?
Realized gain or loss is taken into account for tax purposes.
What is the authority of private letter rulings?
LTRs are the strongest authority for the taxpayer to whom they are issued and the weakest for other taxpayers.
What is a working condition fringe?
Section 132(d): Any property or service provided to an employee of the employer to the extent that, if the employee paid for such property or services, such payment would be allowable under Section 162(trade or business expenses) or Section 167(depreciation).
What is a de minimis fringe?
Section 132e- Any property or service the value of which is (after taking into account the frequency with which similar fringes are provided y the employer to its employees) so small as to make accounting for it unreasonable or administratively impracticable.
How do IRC Section 125 Cafeteria Plans work?
1. Employees may choose from a variety of tax-free fringe benefits
2. If none of the benefits interest them, then employee may be able to take cash instead.
3. Employee is only taxed to the extent that the employee takes cash rather than a tax-free benefit
Can cafeteria plans discriminate in favor of high paid employees?
No
Must the Cafeteria plan be a written plan?
Yes
What is imputed income?
The untaxed economic benefit from the use of the taxpayer’s own property and the taxpayer’s own services.
How are barter transactions taxed?
Each party is taxed on the fair market value of what they receive. In general, informal swaps of services are not taxed unless it is on the level of undermining the tax system.
Are the gains or losses on gifted property taxed?
No
What is amortization?
Depreciation of intangible assets.
How does amortization/ depreciation affect basis?
It decreases an asset’s basis
What is Accelerated Cost Recovery System?
Larger portion of cost is deducted in the early years of the equipment’s useful life
How are the benefits of a life insurance policy taxed?
Benefits are not taxed but premiums are not deductible
What is the tax benefit of life insurance savings?
The interest on the savings element of life insurance is not taxed until money is withdrawn under the policy and not taxed at all if it is withdrawn in the form of a death benefit.
How are annuities taxed?
Purchaser of an annuity is not taxed until the payment is received (§72).
What is the exclusion ration for annuities?
Investment in the annuity/ total expected payments. This fraction of each annuity payment is excluded from income.
What is the tax advantage of an annuity?
1. No tax is paid until you get payments.
2. Taxable gain on the annuity is assigned equally to each payment received even though the actual gain is higher in the early years and lower in the later years.
What happens if you die before you get all of your annuity?
The unrecovered amount can be deducted by your estate
Can employers deduct contributions to qualified pension plans?
Yes, at the time of the contribution
Can an employee borrow from their pension plan?
Yes and there is no penalty but they have to pay back it back. Limits on what can be borrowed.
What does it mean for a net operating loss to be carried forward?
Take amounts business losses in year 1 and apply it in year 2.
What does it mean for a net operating loss to be carried back?
Refile ad deduct losses form year 2 and apply it to profits from year 1
What sort of damages received by judgment or settlement are not taxed?
Damages other than punitive damages on the account of physical injuries or physical sickness.
Is the interest earned on damages taxable?
Yes
What is the basic tax rule regarding loans?
Loan proceeds are not income and loan payments are not deductible.
How is a discharge of indebtedness treated?
Taxed if you had been paid that income.
Does the basis of a property include amounts borrowed to purchase the property?
Yes
What is the gift exception to the forgiveness of debt rule?
If a lender cancels a debt as a gift then the borrower does not have to include the amount canceled as income.
What is the general rule regarding taxation of illegal income?
Illegal income is taxable and expenses associated with it are deductible. (including bribes to foreign officials)
Which expenses associated with earning illegal income are not deductible?
1. Civil and criminal penalties for illegal conduct, including settlements
2. Illegal domestic bribes
3. Expenses associate with drug trafficking
Does the tax liability of a thief for what he steals take precedent over repayment to the victim?
Yes
Who will purchase state and municipal bonds?
Taxpayers with an actual tax rate higher than the putative trax.
How are dividends taxed?
Dividends are added to net capital gains and taxed at capital gains rates
What are arguments in favor of the lower tax rate on corporate dividends?
1. Improves efficiency by reducing the double tax on corporate earnings.
2. Improves efficiency by reducing tax advantages of corporate bonds and corporate stock
What are the arguments against the lower tax rate on corporate dividends?
Wealthy taxpayers receive a disproportionate share of the benefits of the lower rate.
What is the basic rule regarding the sale of a principle residence?
Gross income does not include gain from the sale or exchange of property, if during the 5 year period ending on the date of the sale or exchange such property has been owned and used as principal residence for a period aggregating at least two years
What is the most that can be excluded from the gain on the sale of a principal residence?
$250K (500K joint)
Can like-kind property be exchanged without recognizing a gain?
Yes.
Would an exchange of developed real estate for undeveloped real estate be considered like-kind property?
Yes.
Does a taxpayer always recognize the value of the boot received?
No the taxpayer recognizes the lesser of his gain realized or the boot he receives
In what ways can a stock option be taxed? (i.e. at what points could the tax on stock options be imposed)
1. When the option is received.
2. When the option is sold
3. When the stock is sold
What is the basis taken a spouse transfers property to their spouse or spouse?
They take a substituted basis (the basis of the spouse)
What is the equation for taxable income?
Gross income – above the line deductions = adjusted gross income – below the line deductions – deductions for personal exemptions = taxable income
What are itemized deductions?
Personal deductions that are unrelated to the production of income and are itemized on a separate schedule on the tax return.
What are some itemized deductions?
Casaulty losses,
extraordinary medical expenses,
charitable contributions,
interest on home mortgages,
state and local taxes,
misc deductions (employee business expenses).
What two purposes does the standard deduction serve?